B cells are critical for adaptive immunity, but can also trigger autoimmunity or develop into malignant B cell lymphomas when signaling molecules and/or transcription factors are deregulated. The focus of my Max Eder research group is to understand how signaling perturbations in malignant and normal B cells affect their survival and/or malignant spread in order to find new treatments. A particular focus of our group is to explore whether hyperactivation of signaling pathways could represent a new therapeutic strategy in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). We have shown that acute activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway promotes cell death in transformed mature B cells, namely CLL.
To exploit this therapeutically, we used inhibition of the inhibitory phosphatase SHIP1, which dramatically promotes induction of immunogenic cell death in vitro and in vivo by increasing mitochondrial metabolism and ROS formation in CLL cells (Ecker et al, 2021). Based on these findings, we are currently investigating whether transient inhibition of SHIP1 is effective in drug-resistant CLL and may increase the efficacy of immunotherapeutic approaches to overcome their current limitations in single-agent treatments for CLL.
In a similar effort, we are also investigating the role of dual-specific phosphatases (DUSP proteins) that negatively regulate MAPK signaling in CLL cells. We found that the ERK1/2 phosphatase DUSP6 is highly expressed in samples from CLL patients with poor clinical prognosis, especially in CLL cases carrying MAPK-activating mutations in BRAF and KRAS, and therefore DUSP6 expression may serve as a prognostic marker for CLL. Using global phospho-proteome analysis, we found that inhibition of DUSP1/6 in CLL triggered transient ERK phosphorylation, followed by induction of the DNA damage response pathway and apoptotic cell death specifically in CLL cells. We therefore show that expression of the negative regulators DUSP1 and DUSP6 is required to balance high oncogenic MAPK signaling in CLL and prevent apoptosis (Ecker et al, 2023).
Because activation of the PI3K and MAPK signaling pathways is frequently observed during transformation of CLL cells into aggressive lymphoma, we are currently also investigating how CLL cells overcome the cell death induced by hypersignaling during the transformation process. This information could be useful in finding strategies to prevent and treat Richter's transformation, which is particularly important based on the short survival rate of Richter patients and the lack of effective and targeted treatments.










Alumni
Martina Stumpf (née Braun)
Veronika Ecker
Lisa Kracher (née Brandmeier)
Mar Abril
Lisa Pfeuffer
Maike Buchner obtained her Master's degree in Molecular Medicine from the University of Freiburg in 2006. She went on to complete her PhD with honors in 2010, focusing on the project "Inhibition of Microenvironmental Pathways: a Novel Therapeutic Approach in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia" under the supervision of Hendrik Veelken at the same institution. Her postdoctoral research took her to the University of California, San Francisco, where she worked in the laboratory of Markus Müschen. During this period, Maike Buchner's research centered on the development of normal B cells and their transformation into acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), contributing to pivotal studies on signaling thresholds in ALL and the mechanisms of negative feedback inhibition.
Building on the insights gained from her PhD and postdoctoral studies, Maike Buchner's current research efforts are aimed at understanding the role of various signaling events in the transformation of B cells, with a particular emphasis on chronic lymphocytic leukemia and multiple myeloma. Her research approach involves the analysis of primary patient samples and healthy donors, as well as the use of preclinical models, to explore the effects of inhibiting negative regulatory mechanisms on different cell types. In addition, she is interested in delineating the sequence of events leading to the development of multiple myeloma in mice, with the goal of identifying new therapeutic strategies. In 2023, Maike Buchner achieved her Habilitation at the Technical University of Munich, marking a significant milestone in her academic career. Her work continues to focus on dissecting the complex interplay between divergent signaling pathways in malignant versus normal B cells, particularly downstream of the B cell receptor and in regulating signaling intensity.
Further information on the Buchner lab can be found on the website of the Center for Translational Cancer Research (TranslaTUM)
Decrypting drug actions and protein modifications by dose- and time-resolved proteomics.
Zecha, J., Bayer, F.P., Wiechmann, S., Woortman, J., Berner, N., Muller, J., Schneider, A., Kramer, K., Abril-Gil, M., Hopf, T., Reichart, L., Chen, L., Hansen, F.M., Lechner, S., Samaras, P., Eckert, S., Lautenbacher, L., Reinecke, M., Hamood, F., Prokofeva, P., Vornholz, L., Falcomata, C., Dorsch, M., Schroder, A., Venhuizen, A., Wilhelm, S., Medard, G., Stoehr, G., Ruland, J., Gruner, B.M., Saur, D., Buchner, M., Ruprecht, B., Hahne, H., The, M., Wilhelm, M., Kuster, B. (2023). Science 380, 93-101. doi 10.1126/science.ade3925
Negative feedback regulation of MAPK signaling is an important driver of chronic lymphocytic leukemia progression.
Ecker, V., Brandmeier, L., Stumpf, M., Giansanti, P., Moreira, A.V., Pfeuffer, L., Fens, M., Lu, J., Kuster, B., Engleitner, T., Heidegger, S., Rad, R., Ringshausen, I., Zenz, T., Wendtner, C.M., Muschen, M., Jellusova, J., Ruland, J., Buchner, M. (2023). Cell Rep 42, 113017. doi 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113017
Developmental partitioning of SYK and ZAP70 prevents autoimmunity and cancer.
Sadras, T., Martin, M., Kume, K., Robinson, M.E., Saravanakumar, S., Lenz, G., Chen, Z., Song, J.Y., Siddiqi, T., Oksa, L., Knapp, A.M., Cutler, J., Cosgun, K.N., Klemm, L., Ecker, V., Winchester, J., Ghergus, D., Soulas-Sprauel, P., Kiefer, F., Heisterkamp, N., Pandey, A., Ngo, V., Wang, L., Jumaa, H., Buchner, M., Ruland, J., Chan, W.C., Meffre, E., Martin, T., Muschen, M. (2021). Mol Cell 81, 2094-2111 e9. doi 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.03.043
Targeted PI3K/AKT-hyperactivation induces cell death in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Ecker, V., Stumpf, M., Brandmeier, L., Neumayer, T., Pfeuffer, L., Engleitner, T., Ringshausen, I., Nelson, N., Jucker, M., Wanninger, S., Zenz, T., Wendtner, C., Manske, K., Steiger, K., Rad, R., Muschen, M., Ruland, J., Buchner, M. (2021). Nat Commun 12, 3526. doi 10.1038/s41467-021-23752-2
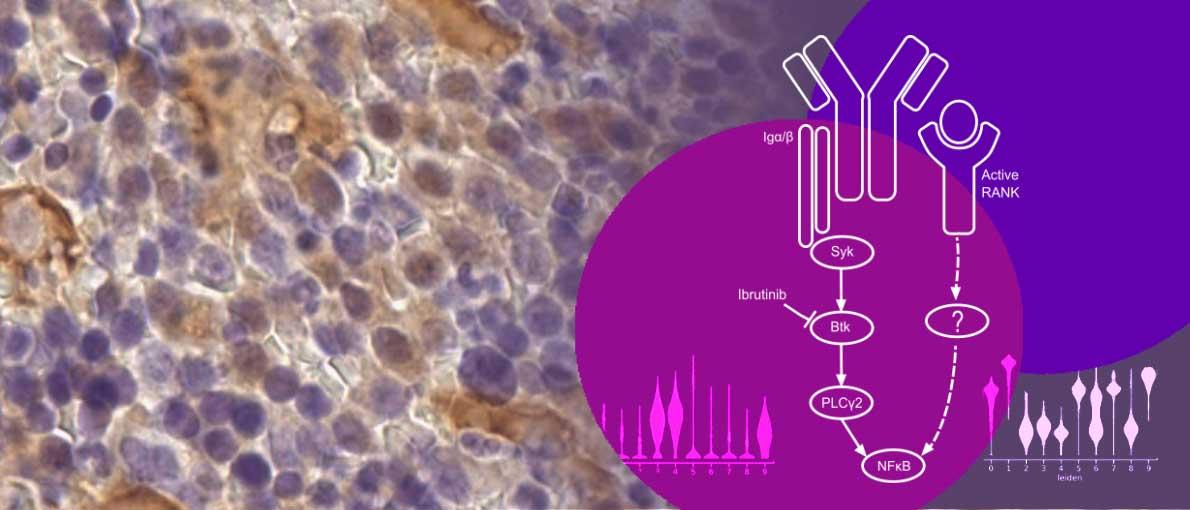
Pathological RANK signaling in B cells drives autoimmunity and chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Alankus, B., Ecker, V., Vahl, N., Braun, M., Weichert, W., Macher-Goppinger, S., Gehring, T., Neumayer, T., Zenz, T., Buchner, M., Ruland, J. (2021). J Exp Med 218, doi 10.1084/jem.20200517
Stromal cell protein kinase C-beta inhibition enhances chemosensitivity in B cell malignancies and overcomes drug resistance.
Park, E., Chen, J., Moore, A., Mangolini, M., Santoro, A., Boyd, J.R., Schjerven, H., Ecker, V., Buchner, M., Williamson, J.C., Lehner, P.J., Gasparoli, L., Williams, O., Bloehdorn, J., Stilgenbauer, S., Leitges, M., Egle, A., Schmidt-Supprian, M., Frietze, S., Ringshausen, I. (2020). Sci Transl Med 12, doi 10.1126/scitranslmed.aax9340
Foxp1 controls mature B cell survival and the development of follicular and B-1 B cells.
Patzelt, T., Keppler, S.J., Gorka, O., Thoene, S., Wartewig, T., Reth, M., Forster, I., Lang, R., Buchner, M., Ruland, J. (2018). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115, 3120-3125. doi 10.1073/pnas.1711335115
PTEN opposes negative selection and enables oncogenic transformation of pre-B cells.
Shojaee, S., Chan, L.N., Buchner, M., Cazzaniga, V., Cosgun, K.N., Geng, H., Qiu, Y.H., von Minden, M.D., Ernst, T., Hochhaus, A., Cazzaniga, G., Melnick, A., Kornblau, S.M., Graeber, T.G., Wu, H., Jumaa, H., Muschen, M. (2016). Nat Med 22, 379-87. doi 10.1038/nm.4062
Erk Negative Feedback Control Enables Pre-B Cell Transformation and Represents a Therapeutic Target in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.
Shojaee, S., Caeser, R., Buchner, M., Park, E., Swaminathan, S., Hurtz, C., Geng, H., Chan, L.N., Klemm, L., Hofmann, W.K., Qiu, Y.H., Zhang, N., Coombes, K.R., Paietta, E., Molkentin, J., Koeffler, H.P., Willman, C.L., Hunger, S.P., Melnick, A., Kornblau, S.M., Muschen, M. (2015). Cancer Cell 28, 114-28. doi 10.1016/j.ccell.2015.05.008
Signaling thresholds and negative B-cell selection in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia.
Chen, Z., Shojaee, S., Buchner, M., Geng, H., Lee, J.W., Klemm, L., Titz, B., Graeber, T.G., Park, E., Tan, Y.X., Satterthwaite, A., Paietta, E., Hunger, S.P., Willman, C.L., Melnick, A., Loh, M.L., Jung, J.U., Coligan, J.E., Bolland, S., Mak, T.W., Limnander, A., Jumaa, H., Reth, M., Weiss, A., Lowell, C.A., Muschen, M. (2015). Nature 521, 357-61. doi 10.1038/nature14231
Mechanisms of pre-B-cell receptor checkpoint control and its oncogenic subversion in acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Swaminathan, S., Chen, Z., Muschen, M. (2015). Immunol Rev 263, 192-209. doi 10.1111/imr.12235
Identification of FOXM1 as a therapeutic target in B-cell lineage acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Buchner, M., Park, E., Geng, H., Klemm, L., Flach, J., Passegue, E., Schjerven, H., Melnick, A., Paietta, E., Kopanja, D., Raychaudhuri, P., Muschen, M. (2015). Nat Commun 6, 6471. doi 10.1038/ncomms7471
Targeting the B-cell receptor signaling pathway in B lymphoid malignancies.
Buchner, M., Muschen, M. (2014). Curr Opin Hematol 21, 341-9. doi 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000048
Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia is driven by antigen-independent cell-autonomous signalling. Duhren-von Minden, M., Ubelhart, R., Schneider, D., Wossning, T., Bach, M.P., Buchner, M., Hofmann, D., Surova, E., Follo, M., Kohler, F., Wardemann, H., Zirlik, K., Veelken, H., Jumaa, H. (2012). Nature 489, 309-12. doi 10.1038/nature11309
The microenvironment differentially impairs passive and active immunotherapy in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia - CXCR4 antagonists as potential adjuvants for monoclonal antibodies. Buchner, M., Brantner, P., Stickel, N., Prinz, G., Burger, M., Bar, C., Dierks, C., Pfeifer, D., Ott, A., Mertelsmann, R., Gribben, J.G., Veelken, H., Zirlik, K. (2010). Br J Haematol 151, 167-78. doi 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2010.08316.x
Spleen tyrosine kinase inhibition prevents chemokine- and integrin-mediated stromal protective effects in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Buchner, M., Baer, C., Prinz, G., Dierks, C., Burger, M., Zenz, T., Stilgenbauer, S., Jumaa, H., Veelken, H., Zirlik, K. (2010). Blood 115, 4497-506. doi 10.1182/blood-2009-07-233692
Spleen tyrosine kinase is overexpressed and represents a potential therapeutic target in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Buchner, M., Fuchs, S., Prinz, G., Pfeifer, D., Bartholome, K., Burger, M., Chevalier, N., Vallat, L., Timmer, J., Gribben, J.G., Jumaa, H., Veelken, H., Dierks, C., Zirlik, K. (2009). Cancer Res 69, 5424-32. doi 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4252



